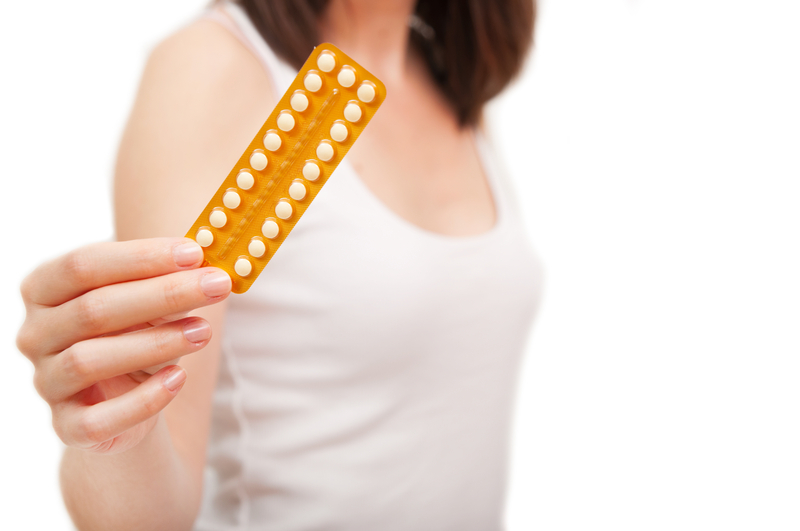
Birth control pills, also known as “the pill,” is a very popular oral contraceptive used to prevent pregnancy. The pill is a very effective form of birth control when taken regularly. It is 99% effective at preventing pregnancy with perfect use, and approximately 91% effective with almost perfect use — which is a more realistic number for most women.
The better you are at taking the pill every day, the more effective it will be, but no method is 100% perfect so it is important to learn more about the pill and proper birth control. This article answers some FAQs about the birth control pill and how to know if the pill is working for you.
What is the Birth Control Pill?
The birth control pill is type of hormonal birth control that needs to be taken orally at the same time every day. It is a very small, round pill that is easy to swallow. Some pills are even chewable!
Combination birth control pills work by delivering a small dose of estrogen and progestin that signals to the body to reduce or stop ovulation, to thicken the cervical mucus to prevent sperm from entering the uterus, and to thin the lining of the uterus to reduce the likelihood that an egg would be able to attach to the uterine lining if it were fertilized.
There are also progestin-only pills, known as the mini-pill, that are a better option for some women, including women who are breastfeeding, are at high-risk for blood clots, or who cannot otherwise take estrogen.
In addition to preventing pregnancy, the pill can lighten or stop your menstrual cycle, help reduce hormonal acne, reduce painful cramping, reduce the risk of ovarian and cervical cancer, treat endometriosis, as well as other reproductive health benefits.
Birth control pills often come in a pill pack that includes four weeks of pills. There is usually three weeks (21 days) of active pills and one week (7 days) of inactive pills or placebo pills. Some pill packs can include 24 days, 90 days, or even up to 365 days of active pills. The active pills and inactive pills are often different colors so it is easy to keep track of where you are in the cycle.
Most women will have a menstrual cycle or spotting while taking the inactive pills and may experience some spotting if taking a pill pack with a longer active pill section.
How Do you Know if the Pill is Working?
Based on what type of pill you are taking and when you start, your doctor can help you figure out how long it will take for your pill to start working.
It can take up to seven days for the combination pill to be effective and up to two days for the progestin-only pill to be effective at preventing pregnancy after you take the first dose. If you have intercourse during this time period after starting the pill, be sure to use another form of contraception to be sure you are protected against unintended pregnancy.
There might not be any obvious external signs that the pill is working, but if you are taking it at the same time every day and not experiencing any adverse side effects then the pill should be effective.
If you are using the pill for other reasons, such as controlling irregular bleeding or hormonal acne, it can take up to four months to see signs that the pill is working. Be patient as your body adjusts to the new treatment and stay consistent with taking it regularly.
Long-term signs that the pill is working might include clearer skin, regular periods, and lighter and less painful periods.
Is it Possible for Birth Control to Not Work?
With perfect use of the birth control pill, it is possible but very unlikely to have an unintended pregnancy. Unintended pregnancies while on the pill can be serious and in case of ectopic pregnancy life-threatening, so call your NYC gynecologist or women’s health professional right away if you have missed a period or think you might be pregnant. Your doctor can discuss emergency contraception and pregnancy test options with you.
Of course, sometimes you forget a pill. If you forget a pill, take it as soon as you remember. If you missed a whole day, take the previous day’s pill plus your regular dose. Be sure to use a backup method of contraception or abstain from intercourse until you’ve gotten back on a regular regimen with your pill pack. It is a good idea to set calendar reminders or an alarm on your phone to help you remember to take your pill each day.
It is recommended to always use a backup birth control method while on the pill, such as condoms, especially if you have any missed pills. It is also important to use a barrier method of birth control, such as condoms, to protect against sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
How Do you Know if your Birth Control isn’t Working for You?
There are many different types of birth control pills so it is possible you will need to try a couple different kinds before you find the one that is right for your body. If you’re experiencing negative side effects from the pill, you may need to switch to another type of pill with different hormone dosages.
If you are experiencing any side effects, such as headaches, nausea, irritability and mood swings, breast tenderness, or abnormal spotting or breakthrough bleeding, speak with your health care provider about your birth control options. These side effects are common and can usually be resolved by a doctor.
If you don’t think birth control pills are working for you and you are interested in trying another method, ask your health care provider about other birth control options such as a hormonal intrauterine device (hormonal IUD), a non-hormonal copper IUD, or a vaginal ring such as the NuvaRing. These options are great for women who struggle with taking the pill on a regular daily basis because they are inserted into the body rather than taken orally. The vaginal ring can be used for three weeks at a time and IUDs can last for years.